Search
Registration Details about Registration When you register you will be asked to register for both the two-day auditorium presentations on days one and

News & Events
New project to train homeless young people as suicide-alert helpersUp to 50 homeless young people will be provided with training to help them recognise suicidal behaviour and make referrals to potentially life-saving resources, thanks to a grant from Suicide Prevention Australia.

News & Events
The impact on childrenThe Aussie summer provides some great opportunities for families to connect in an active and social way. But with it comes a range of factors that can impact on child and family health.

News & Events
Three-continent clinical trial aims to improve survival for aggressive kids’ brain cancerThe Kids Research Institute Australia and Perth Children’s Hospital will lead an international clinical trial of a novel drug combination they hope will increase cure rates for one of the most aggressive forms of childhood brain cancer.

News & Events
Diabetes research the big winner at this year’s Raine AwardsChildren’s Diabetes Centre researchers at The Kids Research Institute Australia are among the big winners of prestigious Raine Medical Research Foundation Awards.

News & Events
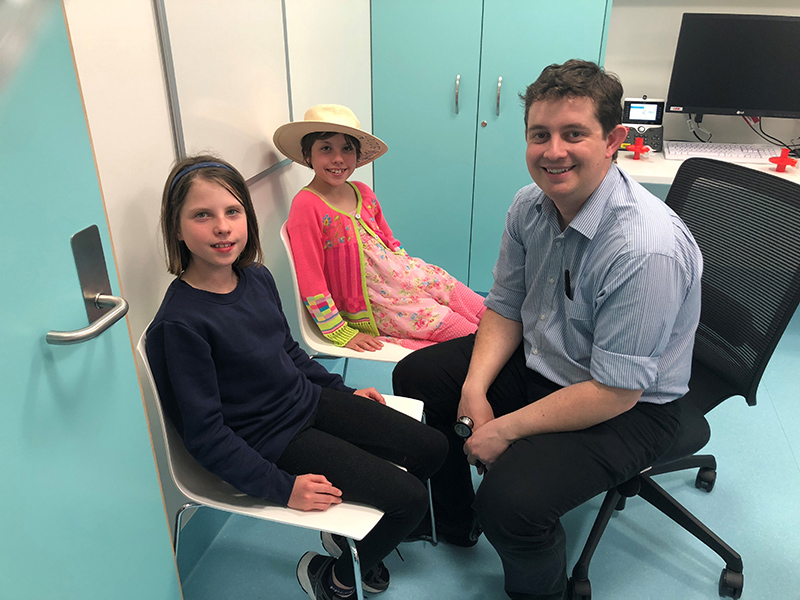
Can a simple urine test predict asthma? New study aims to find outThe Kids Research Institute Australia researchers are investigating whether a simple urine test could predict whether young children with wheezing symptoms will go on to develop asthma.

News & Events
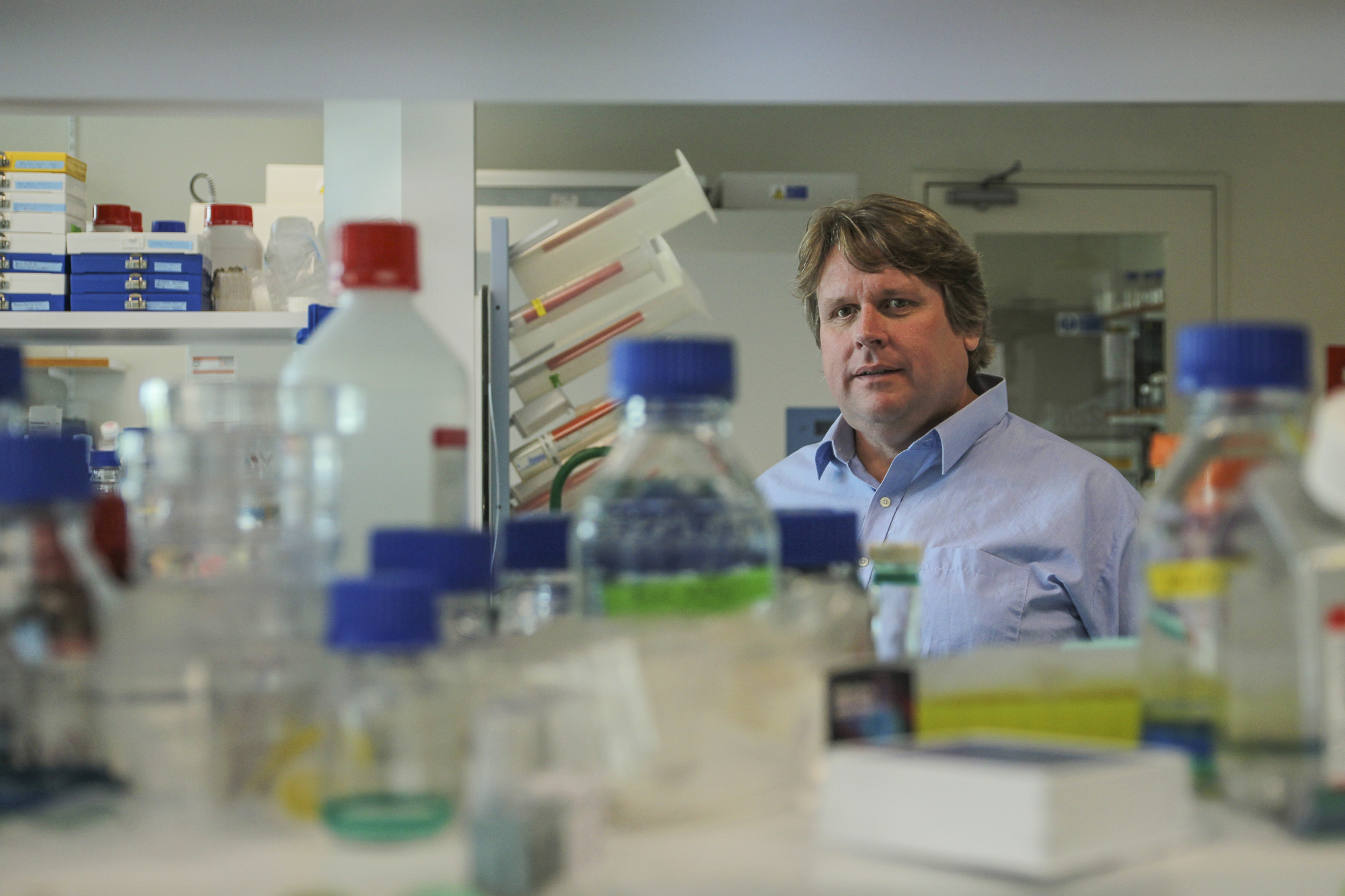
The Kids researchers seek cure for devastating gliomaThe Kids Research Institute Australia’s cancer researchers will use funds raised in the name of a brave three-year-old girl to launch a new assault on the devastating form of childhood cancer which took her life.
News & Events
New screening tool for FASD and ADHD in childrenThe Kids is trialling a new tool for earlier and easier screening of FASD and ADHD in children, using cutting-edge eye-tracking technology developed by the Kids Brain Health Network in Canada.
News & Events
How to win friends and influence people: Cancer researchers talk the talk for big resultsIn the field of cancer research, lobbying efforts by the The Kids Cancer Centre have contributed to major initiatives including Australia’s first personalised medicine program for children with high-risk cancer, and a mission to boost survival rates in brain cancer patients.

News & Events
Northern Territory building on strengthsMEDIA ENQUIRIES Mailing list Media Contacts Be Inspired Please direct general enquiries to our reception on (08) 6319 1000. Please direct media
