Search
Research
Risk factors associated with post-tuberculosis sequelae: a systematic review and meta-analysisPost-tuberculosis (TB) sequelae present a significant challenge in the management of TB survivors, often leading to persistent health issues even after successful treatment. Identifying risk factors associated with post-TB sequelae is important for improving outcomes and quality of life of TB survivors. This systematic review and meta-analysis aims to identify risk factors associated with long-term physical sequelae among TB survivors.
Research
A global mathematical model of climatic suitability for Plasmodium falciparum malariaClimatic conditions are a key determinant of malaria transmission intensity, through their impacts on both the parasite and its mosquito vectors. Mathematical models relating climatic conditions to malaria transmission can be used to develop spatial maps of climatic suitability for malaria. These maps underpin efforts to quantify the distribution and burden of malaria in humans, enabling improved monitoring and control.
Research
Mapping fertility rates at national, sub-national, and local levels in Ethiopia between 2000 and 2019Fertility rates are key indicators of population health and demographic change, influencing economic development, healthcare planning, and social policies. Understanding subnational variation in fertility rate is important for effective geographical targeting and policy prioritization. This study aimed to identify geographic variation, trends, and determinants of fertility rates in Ethiopia over the past two decades.
Research
Mapping the incidence rate of typhoid fever in sub-Saharan AfricaWith more than 1.2 million illnesses and 29,000 deaths in sub-Saharan Africa in 2017, typhoid fever continues to be a major public health problem. Effective control of the disease would benefit from an understanding of the subnational geospatial distribution of the disease incidence.
Research
Neighborhood Places for Preschool Children's Physical Activity: A Mixed-Methods Study Using Global Positioning System, Geographic Information Systems, and Accelerometry DataThis study adds to the current literature by using a novel device-based method to explore where preschool children are physically active outside of home and childcare settings. This study combined accelerometry with geospatial data to explore the influence of the environment on preschool children's physical activity by objectively identifying the locations where preschool children engage in moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA) within and outside of their neighborhood.
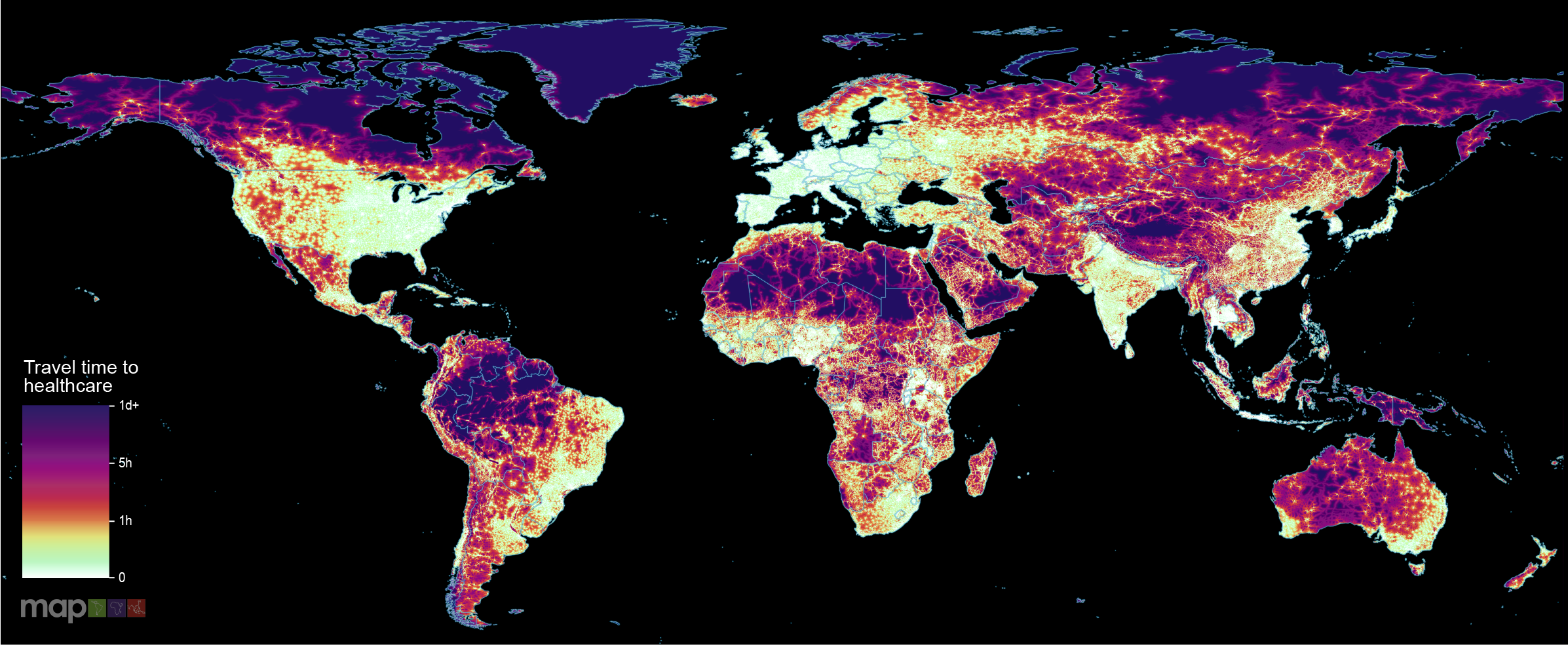
News & Events
World-first maps reveal how long it takes to reach healthcare from anywhere in the globeNew research which maps the entire global population’s travel time to their nearest healthcare facility has revealed major inequalities in access to healthcare depending on whether people have access to motorised transport or not.
Research
Spatiotemporal patterns of influenza in Western AustraliaUnderstanding the geospatial distribution of influenza infection and the risk factors associated with infection clustering can inform targeted preventive interventions. We conducted a geospatial analysis to investigate the spatial patterns and identify drivers of medically attended influenza infection across all age groups in Western Australia.
Research
Comparison of new computational methods for spatial modelling of malariaGeostatistical analysis of health data is increasingly used to model spatial variation in malaria prevalence, burden, and other metrics. Traditional inference methods for geostatistical modelling are notoriously computationally intensive, motivating the development of newer, approximate methods for geostatistical analysis or, more broadly, computational modelling of spatial processes.
Research
Mapping the global prevalence, incidence, and mortality of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax malaria, 2000-22: a spatial and temporal modelling studyMalaria remains a leading cause of illness and death globally, with countries in sub-Saharan Africa bearing a disproportionate burden. Global high-resolution maps of malaria prevalence, incidence, and mortality are crucial for tracking spatially heterogeneous progress against the disease and to inform strategic malaria control efforts. We present the latest such maps, the first since 2019, which cover the years 2000–22. The maps are accompanied by administrative-level summaries and include estimated COVID-19 pandemic-related impacts on malaria burden.
Research
Quantifying undetected tuberculosis in Ethiopia using a novel geospatial modelling approachTuberculosis (TB) is the leading infectious cause of death globally, with approximately three million cases remaining undetected, thereby contributing to community transmission. Understanding the spatial distribution of undetected TB in high-burden settings is critical for designing and implementing geographically targeted interventions for early detection and control.
